Opinion: Menopause doesn’t have to be miserable
- Share via
There are an estimated 55 million women in menopause in the United States today, the majority of whom endure its most debilitating symptoms in silence. It doesn’t have to be so debilitating, and it wouldn’t be if we could end the silence and make even a handful of key policy changes.
Menopause has long been neglected by the mainstream medical establishment as well as by lawmakers, employers, even the media. All have failed to help women navigate this inevitable life stage. New data from the Mayo Clinic show that the burden extends far beyond the physical and physiological effects and also has huge economic consequences, with an estimated $1.8 billion in lost earnings for menopausal women per year.
There was a bit of encouraging news last month: The Food and Drug Administration approved a new non-hormonal oral drug to treat vasomotor symptoms of menopause — better known as hot flashes. As many as 80% of women experience hot flashes, with a disproportionate effect on Black women, for whom the symptoms of menopause last longer and are experienced more intensely. Among the profound short- and long-term health consequences of hot flashes are sleep disruption, mood disturbances, brain fog and increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
Those who suffer from hot flashes deserve innovation and investment in a wide array of options, such as this latest market entry, a pill to be sold under the trade name Veozah. We are heartened to see the FDA clear the path for new treatments. But this move also calls for an urgent caveat — and a broader call to action.
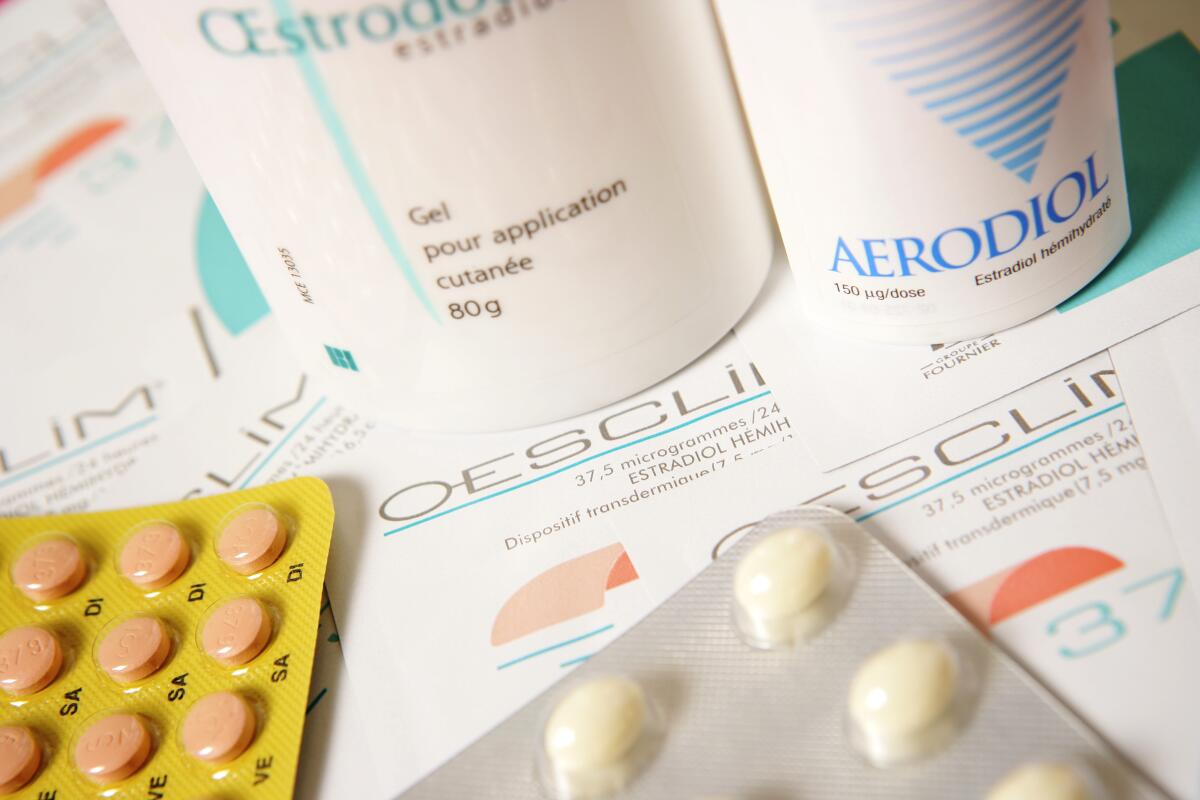
It is imperative that attempts to promote sales of Veozah do not pit it against or present it as a safer, superior option to estrogen and estrogen-progestin therapy, also known as menopause hormone therapy. A decades-old study misrepresented and overgeneralized the risks of hormone therapy, creating unfounded fears for an entire generation.
Simply but emphatically stated: Hormone therapy is not only the most effective treatment for hot flashes, but also the most cost-effective one. For symptomatic women who initiate hormone therapy before age 60 or within 10 years of their last period, the North American Menopause Society, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and many other national and international organizations agree that the benefits outweigh the risks.
Hormone therapy also has long-term health benefits. It prevents osteoporosis, decreases the risk of Type 2 diabetes, and treats the genitourinary syndrome of menopause, symptoms of which include painful sex, urinary urgency and frequent recurrent urinary tract infections. Other than treating hot flashes, additional benefits of Veozah, if any, and the long-term safety profile are unknown.
It is true that not everyone is a candidate for hormone therapy, including those with a personal history of breast or uterine cancer, a history of heart attack or stroke, or an increased risk for developing blood clots. But for millions in need of relief, hormones can and should be a first-line option.
Correcting the overblown fears of hormone therapy requires an immediate course correction. We recommend three concrete reforms as a starting point.
First, the National Institutes of Health must not only clarify current data and retract its prior warnings, but also design and begin a new modern initiative that can assess the long-term benefits of hormone therapy and accurately assess its risks. This is a move that can be directed and funded by Congress: Last fall, for the first time, Congress stepped up and introduced the Menopause Research Act of 2022 to initiate this very process; an updated version of the bill will be introduced in the near future.
Second, the FDA must end its outdated requirement to label all estrogen products with a “black box warning.” That mandate is based on widely misinterpreted data in older populations who were using systemic estrogen. It would be reasonable to remove the warning from low-dose vaginal estrogen products.
And third, menopause treatments need to be accessible and affordable for everyone — meaning that all private and public health insurance programs must ensure coverage. This mandate applies especially to Veozah, which will cost a hefty $550 for a 30-day supply. (Hormone therapy runs $30 to $90 per month.)
Menopause policy should be about equity — health, economic, age and gender — and enabling people to make truly informed decisions and live their best lives. It requires robust public discourse, thorough and transparent research, and a firm political commitment to prioritize women’s full and fair representation at all ages and life stages.
Jennifer Weiss-Wolf is the executive director of NYU Law’s Birnbaum Women’s Leadership Network and the author of “Periods Gone Public: Taking a Stand for Menstrual Equity.” Sharon Malone is the chief medical advisor of the telehealth company Alloy Women’s Health.
More to Read
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.